Web API 2 With Entity Framework 6 Code First Migrations
In this article, i will show you, crud operation code first approach in ASP.NET MVC entity framework:
1. I am using Visual Studio 2017. Open the Visual Studio and add a new project.
2.Choose the “Web” option in installed templates and choose “ASP.NET Web Application (.NET Framework)”. Give the proper name of project. and select .net framework. Then click on OK.
3.When you click OK, you’ll be prompted to choose the type of ASP.NET Web Application. Choose Web API and click OK.
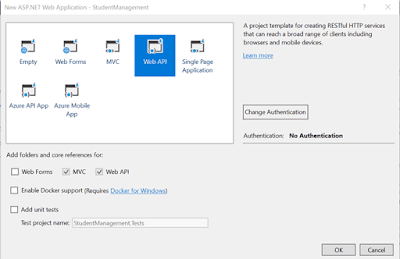
- Install this package from Tools menu-> nuget package manger-> Package manager console-> Install-Package EntityFramework
Entity Framework Code First Migrations
- Open Package Manager Console and select the default project as your WebAPI project. Type the command Enable-Migrations and press enter.
- Once the command is executed, it does some changes to our solution. As a part of adding migrations, it creates a Migrations folder and adds a class file named ”Configuration.cs”. This class is derived from DbMigrationsConfiguration class.
- The context parameter is the instance of our context class that got generated while we were adding a controller. We provided the name as StudentManagementContext. This class derives from DbContext class. This context class takes care of DB schema and the DbSet properties of this class are basically the tables that we’ll have when our database will be created. It added Students as a DbSet property that returns our Student model/entity and would be directly mapped to the table that will be generated in the database.
- The next step is to execute the command named “Add-Migrations”. In the package manager console, execute this command with a parameter of your choice that would be the name of our first migration. I call it ”Initial”. So, the command would be Add-Migrations Initial.
- Again in the package manager console, run the command “Update-Database”.
Let’s see what we got in our database when the earlier command got successfully executed.
- Since we used the local database, we can open it by opening Server Explorer from the View tab in Visual Studio itself.
- Once the Server Explorer is shown, we can find the StudentManagementContext database generated and it has two tables named Students and __MigrationHistory. Students table corresponds to our Student model in the code base and __MigrationsHistory table is the auto-generated table that keeps track of the executed migrations.




